What is an IP Address – Definition and Explanation
An IP address is a unique address that identifies a device on the internet or a local network. In essence, IP addresses are the identifier that allows information to be sent between devices on a network: they contain location information and make devices accessible for communication.
IP Stands for INTERNET PROTOCOLS(IP)
- (TCP/IP) – communicate between networks and devices.
- Typical home networks -start with 192.168.
- IP addresses are especially important for sending and receiving information.
- The IP address 192.168. 0.1 is one of 17.9 million private addresses, and it’s used as the default router IP address for certain routers, including some models from Cisco, D-Link, LevelOne, Linksys, and many others.
- IEEE 802.11-INTERNET STANDARD FOR WIFI
What Does Internet Protocol Address (IP Address) Mean?
An Internet Protocol address (IP address) is a logical numeric address that is assigned to every single computer, printer, switch, router or any other device that is part of a TCP/IP-based network.
The IP address is the core component on which the networking architecture is built; no network exists without it. An IP address is a logical address that is used to uniquely identify every node in the network. Because IP addresses are logical, they can change. They are similar to addresses in a town or city because the IP address gives the network node an address so that it can communicate with other nodes or networks, just like mail is sent to friends and relatives.
The numerals in an IP address are divided into 2 parts:
- The network part specifies which networks this address belongs to and
- The host part further pinpoints the exact location
How to find IP Address in your Computer/Laptop?
Step 1: Go to Windows Icon in your Computer
Step 2: Type ‘Command Prompt’ in Search Bar
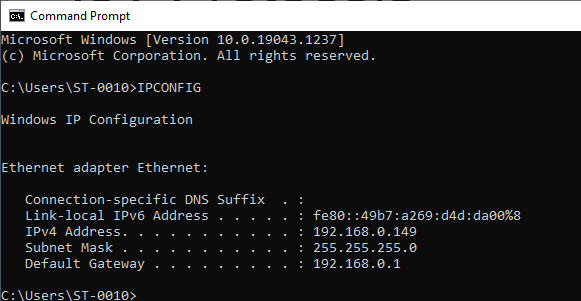
Step 3: Type ’IPCONFIG’ in Command Prompt
OUTPUT OF WINDOWS IP CONFIGURATION
STRYDO Explains Internet Protocol Address (IP Address)
An IP address is the most significant and important component in the networking phenomena that binds the World Wide Web together. The IP address is a numeric address assigned to every unique instance that is connected to any computer communication network using the TCP/IP communication protocols.
Network nodes are assigned IP addresses by the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol server as soon as the nodes connect to a network. DHCP assigns IP addresses using a pool of available addresses which are part of the whole addressing scheme. Though DHCP only provides addresses that are not static, many machines reserve static IP addresses that are assigned to that entity forever and cannot be used again.
IP addresses falls into two types:
- Classfull IP addressing is a legacy scheme which divides the whole IP address pools into 5 distinct classes—A, B, C, D and E.
- Classless IP addressing has an arbitrary length of the prefixes.
Look into other topics too
/*54745756836*/




